Accueil du site > Production scientifique > Concomitant EDD and EID of DNA evidenced by MSn and double resonance experiments
Concomitant EDD and EID of DNA evidenced by MSn and double resonance experiments
Date de publication: 20 février 2011
V.H. Nguyen, C. Afonso, J.-C. Tabet
Int. J. Mass Spectrom. (2011). DOI
Travail réalisé sur le site de l’Université Paris 6.
Abstract
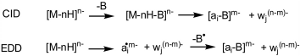
Under collisional activation condition, it is well known that dissociations of multideprotonated oligonucleotides involve an initial loss of nucleic base (formation of [M-nH-Bi]n-) yielding consecutively the complementary (ai-B) and wj product ions. The loss of thymine is thermodynamically unfavored owing to its low proton affinity. 6mer DNA anions were activated in SORI-CID and by EDD. The EDD spectra are significantly different from SORI-CID. All EDD spectra showed singly charged w5- with good abundance, while this ion was not detected in SORI-CID spectra. In EDD spectra loss of thymine is easily detected, surprisingly doubly charged fragment ions were also detected, these ions can be produced directly from precursor ion [M-2H]2-. MS3 and double resonance experiments have been realized to find the origin of these doubly charged and [ai-T]- ions in EDD spectra of d(T2AT3) and (T2CT3). It has been demonstrated that these doubly charged ions are produced by electron induced dissociation. The combination of double resonance and EDD/SORI-CID MS3 experiments allows decoupling the EID from the EDD processes.








