Accueil du site > Production scientifique > Vibrational spectroscopy of deprotonated peptides containing an acidic side chain
Vibrational spectroscopy of deprotonated peptides containing an acidic side chain
Date de publication: 3 octobre 2018
E . Nicol, C. Clavaguéra, G. Ohanessian
Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 435 42-50 (2019). DOI
Travail réalisé sur le site de l’Université Paris Sud.
Abstract
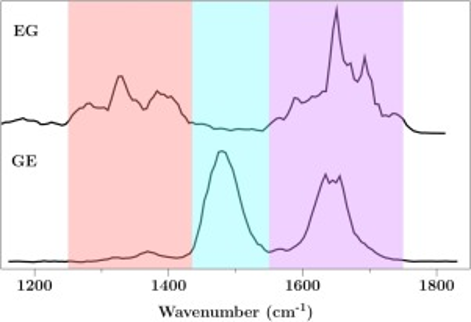
The vibrational properties of four deprotonated dipeptides and three tripeptides containing an acidic residue, either Asp or Glu, have been studied using InfraRed Multiple Photon Dissociation (IRMPD) action spectroscopy in a mass spectrometer. It is found that these spectra fall into two broad categories, including clearly different spectra for sequence-reversed pairs of dipeptides. The observed bands were assigned using Density Functional Theory (DFT) calculations. Aside from the bands pertaining to the CO stretching modes which all lie in the expected 1550–1750 cm−1 range, photon absorption is strongly influenced by the hydrogen bonding patterns, which differ according to whether the acidic residue is located at the C-terminus or not. This leads to two distinct frequency ranges of absorption in between 1250 and 1550 cm−1. In addition, unexpectedly wide absorption around 1600 cm−1 may be attributed to non-classical proton sharing between the two carboxylates when Asp is at the C-terminus.








